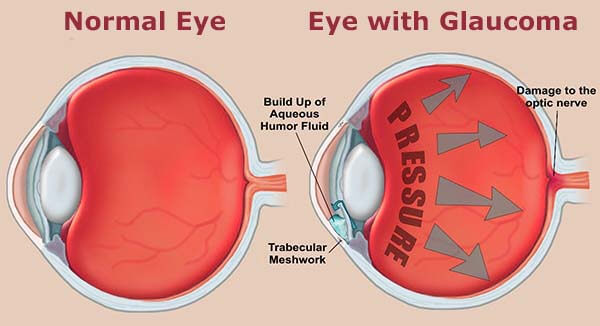
Glaucoma is typically known as a singular eye condition that is more common among the elderly. It is a collection of diseases that shows itself in more than one ways. Although treatable, glaucoma can cause permanent damage to the optical nerve tissue, which can even result in blindness. While the effects of a damaged nerve are more common in older people, symptoms and warning signs can be detected at an early age. Early detection is the key to controlling and preventing the damage from spreading.
There are primarily two most common types of glaucoma: angle-closure glaucoma and open-angle glaucoma. Many people experiencing open-angle glaucoma do not feel vision loss since the initial loss is of peripheral or side vision, and the sharpness or visual acuity of vision is maintained until late the condition. By the time the individual realizes the degree of the damage, it has become irreversible, even with the help of surgery. Because open-angle glaucoma is silent but deadly, it is important to visit a doctor regularly for checkups.
Unlike open-eye glaucoma, acute angle closure glaucoma happens suddenly and causes extreme pain and rapid vision loss. If you wear prescription glasses, it becomes hard to determine whether the deteriorating vision is due to age or a result of something more serious. Of course, the best way of dealing with this problem would be to see your doctor on a regular basis and also be on the lookout for different glaucoma signs and symptoms. Listed below are some important signs that may be of great help in determining if you have glaucoma.
- Blurred Or Hazy Vision/ Alteration In Your Peripheral Vision: If you notice a significant change in your vision field or can’t see anything to the left or right even when the object is right in front of you, you may have glaucoma.
- Appearance of rainbow colored circles around bright lights
- Experiencing tunnel vision. Tunnel vision is a great way to detect glaucoma, since everything you see appears as though you are looking at it through a tunnel.
- Dull pain in either eye. Keep in mind that glaucoma is typically not painful at first but can develop overtime. Even if you are experiencing slight pain in either of your eyes, it is better to get it checked at the earliest possible stage.
- Vomiting or nausea (accompanied with serious eye pain)
- Unexpected sight loss
- Experiencing eye pressure. In angle-closure glaucoma, the closed angle causes the eye nerve to become strained, which can cause sudden vision loss. This suddenly increasing eye pressure is a sign of glaucoma and should be dealt with immediately.
What to Do If You Are Diagnosed With Glaucoma?
Once diagnosed with glaucoma, it is important to set a schedule of tests with your eye doctor to examine your condition and ensure your prescribed eye treatment is successfully keeping up an optimum eye pressure and health in general.